How long is cord blood useful?
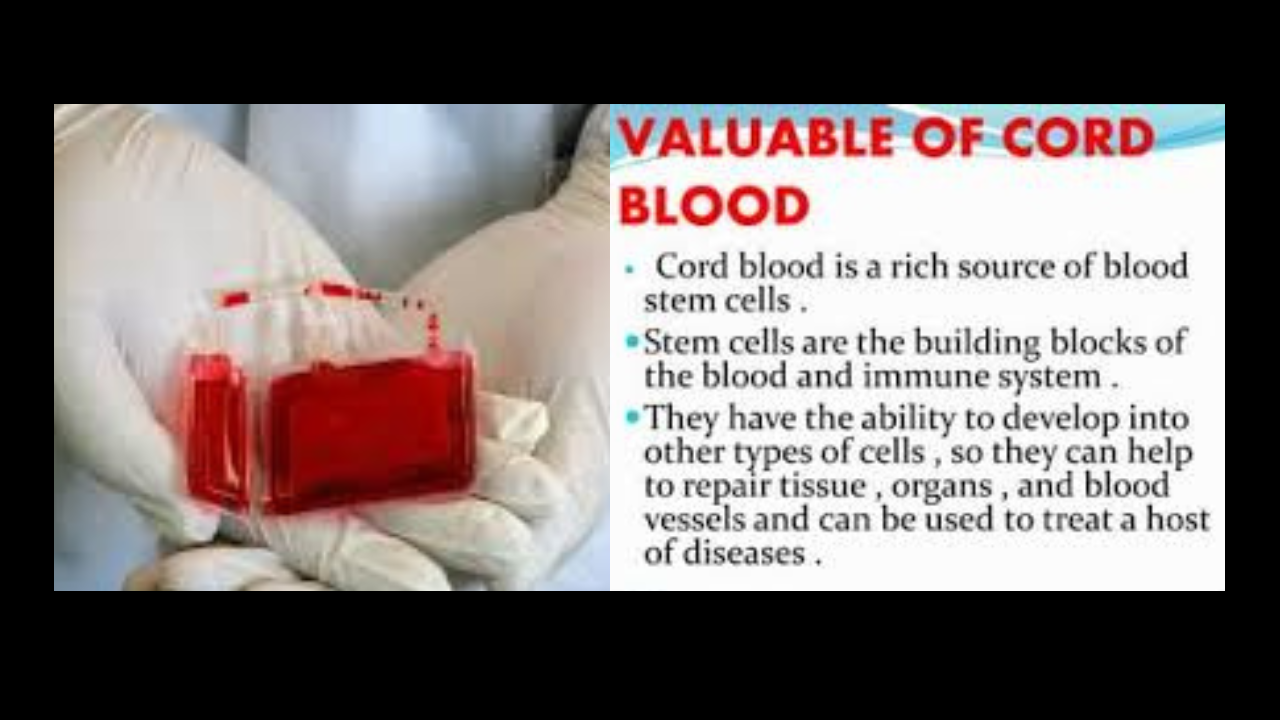
How long is cord blood useful? What is Cord Blood? The blood that is left in the placenta and umbilical cord after childbirth is known as cord blood. This blood is a rich source of stem cells that can be used in various medical treatments and therapies. Cord blood is collected immediately after delivery, processed,