Diabetes Symptoms: Early Signs, Causes, and How to Manage Them
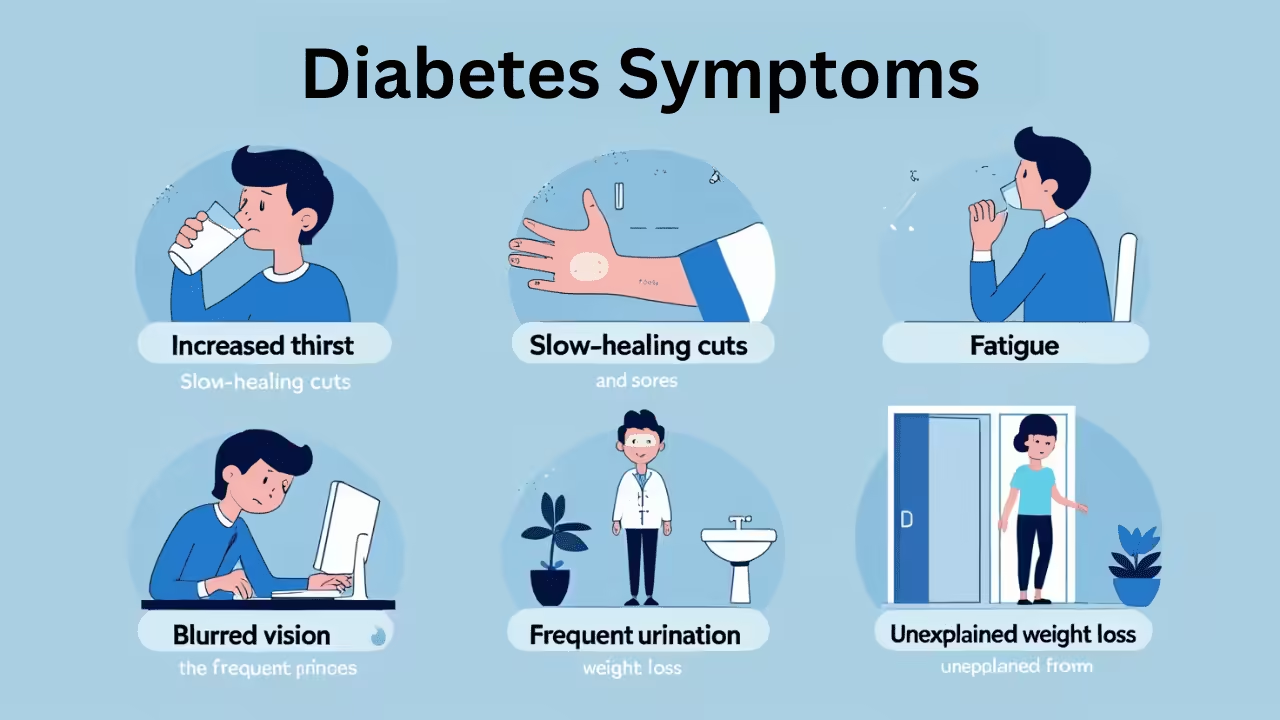
Diabetes Symptoms: Early Signs, Causes, and How to Manage Them Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes The symptoms of diabetes may vary from person to person, but most of the signs often include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. You should consider checking yourself for diabetes if you always feel tired, your vision becomes