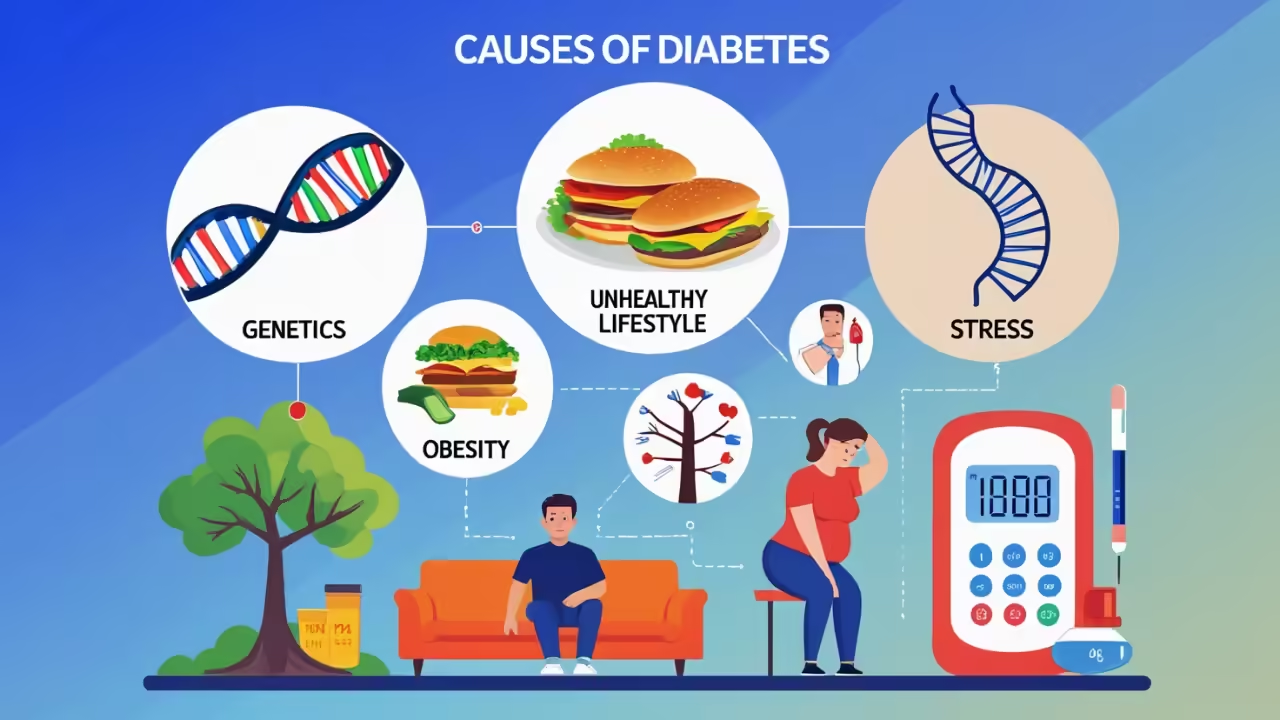
Understanding the Causes of Diabetes: Key Factors and Prevention Tips
Understanding the Causes of Diabetes: Key Factors and Prevention Tips Causes of Type 1 Diabetes Type 1 diabetes, also referred to as insulin-dependent diabetes, results mainly due to an autoimmune attack in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and kills the beta cells responsible for producing insulin inside the pancreas. This destruction lowers the