The True Definition of Diabetes: What Diabetes is Most Accurately Defined As
The Origin of Diabetes
Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood, has puzzled medical experts for centuries. The name “diabetes” itself stems from the Greek word for “siphon,” alluding to the frequent urination associated with the disease. While the exact origin of diabetes remains elusive, researchers have made significant strides in understanding its complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. With the advent of innovative medications like Trulicity and a deeper comprehension of diabetes symptoms, the quest to unravel the origin of this multifaceted condition continues to evolve.
Multiple theories have been postulated to elucidate the origins of diabetes, ranging from autoimmune dysfunction to insulin resistance. One prevailing notion is that diabetes may have origins dating back to ancient civilizations, where descriptions of excessive thirst and recurrent urination akin to diabetes symptoms were documented. Modern research endeavors explore the intricate mechanisms underlying the onset and progression of diabetes, shedding light on the intricate pathways that govern glucose metabolism and insulin regulation. As the enigmatic origins of diabetes unravel, advancements in medical science and technology hold promise for enhanced interventions and management strategies to alleviate the burden of this prevalent global health concern.
- One prevailing notion is that diabetes may have origins dating back to ancient civilizations
- Descriptions of excessive thirst and recurrent urination akin to diabetes symptoms were documented in ancient texts
- Modern research endeavors explore the intricate mechanisms underlying the onset and progression of diabetes
- Advancements in medical science and technology hold promise for enhanced interventions and management strategies
Understanding the Physiology of Diabetes
The physiology of diabetes involves an intricate interplay between insulin and glucose within the body. When someone has diabetes, their body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to use insulin effectively.The pancreas secretes the hormone insulin, which aids in controlling blood sugar levels.. Without enough insulin or with inefficient use of insulin, blood sugar levels can become elevated, leading to various complications. For instance, medications like Farxiga and Toujeo can help manage blood sugar levels, but they may also come with potential side effects that should be monitored by a healthcare provider such as an endocrinologist.
Understanding how diabetes affects the body’s physiology is crucial for effective management and treatment. From monitoring blood sugar levels to making dietary and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with diabetes must work closely with healthcare professionals to optimize their health. Consulting with an endocrinologist can provide specialized guidance and support in navigating the complexities of diabetes care, ensuring a comprehensive approach to treatment while managing potential medication side effects such as those associated with Farxiga or Toujeo.
- Diabetes involves an interplay between insulin and glucose in the body
- Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels
- Lack of insulin or ineffective use can lead to elevated blood sugar levels
- Elevations in blood sugar can lead to complications.
- Medications like Farxiga and Toujeo can help manage blood sugar levels but may have side effects that need monitoring
Understanding how diabetes impacts the body’s physiology is essential for effective management. This includes monitoring blood sugar, making lifestyle changes, and working closely with healthcare professionals. Endocrinologists can provide specialized guidance in managing diabetes care comprehensively while addressing potential medication side effects such as those associated with Farxiga or Toujeo.
The Different Types of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, results from the immune system attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune response leads to a lack of insulin production, requiring daily insulin injections for survival. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes symptoms typically develop in adulthood and are usually related to a combination of genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors, such as poor diet and sedentary behavior. Medical management for type 2 diabetes often involves oral medications, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, insulin therapy, such as Lantus insulin, to help control blood sugar levels.
Individuals with type 1 diabetes rely on multiple daily insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their condition, while those with type 2 diabetes may initially respond to oral medications and lifestyle changes. In more advanced cases of type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy might be necessary to achieve optimal blood sugar control. It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and goals for managing the condition effectively.
- Children and adolescents are frequently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
- The outcome of the immune system targeting the pancreatic cells that produce insulin.
- Requires daily insulin injections for survival
- Type 2 diabetes symptoms typically develop in adulthood
- Usually related to a combination of genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors
- Medical management for type 2 diabetes involves oral medications, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes insulin therapy like Lantus insulin
Individuals with type 1 diabetes rely on multiple daily insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their condition. On the other hand, those with type 2 diabetes may initially respond to oral medications and lifestyle changes. However, more advanced cases of type 2 diabetes might require insulin therapy to achieve optimal blood sugar control. It is essential for individuals with any form of diabetes to collaborate closely with healthcare providers to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and goals for effectively managing the condition.
Risk Factors for Developing Diabetes
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing diabetes include a family history of the disease, particularly if a sibling or parent has been diagnosed. Being overweight or obese significantly raises the risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to the impact excess body weight has on blood sugar levels. Low levels of physical activity and poor dietary choices can also contribute to the development of diabetes, as they can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Individuals with prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes, are at an increased risk of developing the disease. Inadequate sleep and high-stress levels have also been linked to a higher risk of diabetes. Additionally, certain medications, such as corticosteroids and antipsychotics, can raise blood sugar levels and increase the likelihood of developing diabetes.
- Family history of diabetes
- Overweight or obesity
- Low physical activity levels
- Poor dietary choices
- Prediabetes condition
- Inadequate sleep
- High-stress levels
- Certain medications such as corticosteroids and antipsychotics
Symptoms and Signs of Diabetes
Diabetes can manifest through a variety of symptoms that are important to recognize for early detection and management. Fluctuating glucose levels can lead to excessive thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight changes. For individuals predisposed to diabetes, it is crucial to get real about the potential signs and seek medical advice promptly to establish a treatment plan.
Managing diabetes goes beyond controlling glucose levels; it also involves lifestyle adjustments and monitoring. Some individuals may require insulin pumps for effective management. Recognizing the signs early and utilizing the appropriate tools can significantly improve the quality of life for those living with diabetes.
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight changes
Managing diabetes involves:
- Lifestyle adjustments
- Monitoring glucose levels
- Potential need for insulin pumps
Early recognition of symptoms and proper management can improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Diagnosing Diabetes
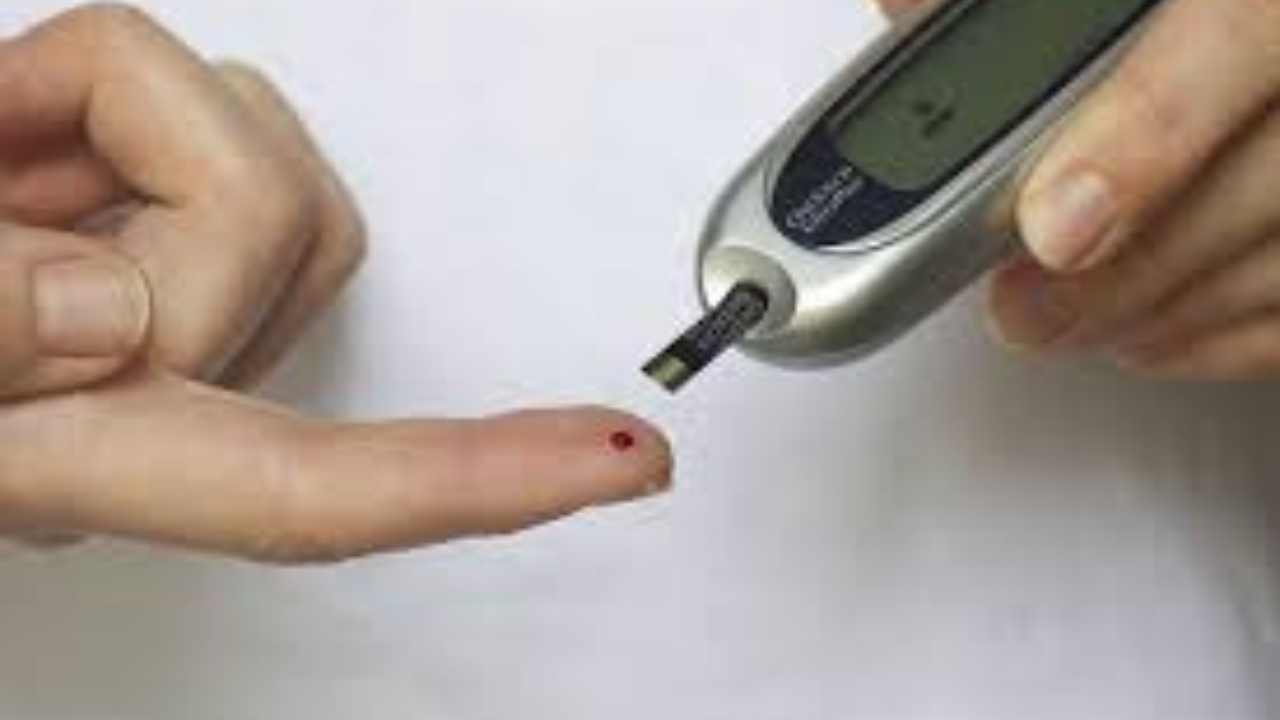
When it comes to diagnosing diabetes, it is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of the disease. In individuals with prediabetes, symptoms may not always be evident, making regular blood sugar monitoring essential for early detection. Devices like the Dexcom G7 continuous glucose monitoring system can be valuable tools in tracking blood sugar levels and identifying fluctuations that may point toward the development of diabetes. Additionally, individuals experiencing symptoms such as frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, or extreme thirst should consult a healthcare provider promptly for further evaluation.
In some cases, complications associated with diabetes may also serve as red flags during the diagnostic process. For instance, the presence of macular edema, a common complication of diabetes that affects the eyes, may prompt healthcare professionals to investigate further for underlying diabetic conditions. By recognizing these warning signs and conducting appropriate tests like fasting blood sugar tests or oral glucose tolerance tests, healthcare providers can diagnose diabetes accurately and implement timely interventions to manage the condition effectively.
- Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for early detection of diabetes
- Devices like the Dexcom G7 continuous glucose monitoring system can help track blood sugar levels
- Symptoms such as frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, or extreme thirst should prompt consultation with a healthcare provider
- Complications associated with diabetes, such as macular edema, can serve as red flags during diagnosis
- Healthcare providers may conduct fasting blood sugar tests or oral glucose tolerance tests to accurately diagnose diabetes
Complications Associated with Diabetes
One of the key complications that can arise from uncontrolled diabetes is damage to the blood vessels throughout the body. High blood sugar levels over time can lead to a condition called atherosclerosis, where the blood vessels become narrowed and hardened. This can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. The reduced blood flow caused by atherosclerosis can also result in poor wound healing, especially in the extremities, which can lead to infections and, in severe cases, amputation.
Another complication associated with diabetes is diabetic neuropathy, a type of nerve damage that can affect various parts of the body. Insulin is essential for nerve health, and when diabetes interferes with its proper function, nerves can become damaged over time. This can result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain in the affected areas. Diabetic neuropathy can impact the nerves that control vital functions such as digestion, bladder control, and blood pressure regulation, leading to further complications and reducing the individual’s quality of life.
- Damage to the blood vessels throughout the body
- Atherosclerosis can lead to heart disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease
- Reduced blood flow can result in poor wound healing and potential amputation
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Nerve damage affecting various parts of the body
- Symptoms include numbness, tingling, or pain
- Impact on vital functions such as digestion and bladder control
Treatment Options for Diabetes
Treatment options for diabetes mainly focus on controlling blood sugar levels to prevent complications. One common method is the use of insulin, which helps regulate glucose levels in the body. Insulin can be administered through injections or insulin pumps, depending on the individual’s needs.
Another treatment option is medication, such as oral hypoglycemic agents, which help the body utilize insulin more effectively. These drugs have the potential to reduce blood sugar levels and enhance glycemic management in general. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise, play a crucial role in managing diabetes. By combining medication with proper diet and exercise, individuals can effectively manage their diabetes and lead a healthier life.
- Insulin therapy is a common method to regulate glucose levels
- Medications like oral hypoglycemic agents can improve insulin utilization
- Lifestyle modifications such as healthy diet and regular exercise are crucial for diabetes management
Preventative Measures for Diabetes
Preventative measures for diabetes mainly revolve around adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a balanced diet that is low in sugar and processed foods while being rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Regular physical activity is also crucial in preventing diabetes, with the aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week. It is vital to maintain a healthy weight as obesity is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. By making small, sustainable changes to one’s daily routine, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or going for a brisk walk after dinner, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing diabetes.
In addition to diet and exercise, monitoring blood sugar levels and managing stress are also key preventative measures for diabetes. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help identify any potential issues early on and allow for timely intervention. Stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Taking proactive steps toward one’s health, such as quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption, can further lower the risk of developing diabetes and its complications in the long run.
- Maintain a balanced diet low in sugar and processed foods
- Make sure your meals contain whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Make an effort to exercise for at least 30 minutes on most days of the week.
- Maintain a healthy weight to lower the risk of type 2 diabetes
- Make small sustainable changes to daily routine for better health
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly
- Manage stress through deep breathing exercises or meditation
- Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help identify issues early on
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption for better overall health
Living with Diabetes: Tips and Strategies for Management
Managing diabetes requires a proactive approach that integrates lifestyle modifications and medical adherence. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole foods and low in processed sugars, as well as engaging in regular physical activity are essential components of controlling blood glucose levels. Additionally, establishing a consistent routine for medication intake and regular check-ups with healthcare providers can aid in preventing complications associated with diabetes.
Incorporating stress-reducing activities such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can contribute to overall well-being and help in managing diabetes more effectively. Seeking support from family, and friends, or joining diabetes support groups can provide emotional support and valuable insights into coping with the challenges that come with the condition. It is crucial to stay informed about diabetes management strategies and continually educate oneself on the latest advancements in diabetes care.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly
- Continue to eat a healthy, whole-food-rich diet.
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Create a regular schedule for taking your medications.
- Attend regular check-ups with healthcare providers
Incorporating stress-reducing activities such as:
- Mindfulness meditation
- Yoga
- Engaging in hobbies
Seeking support from:
- Family
- Friends
- Diabetes support groups
Stay informed about diabetes management strategies by:
- Educating oneself on the latest advancements in diabetes care
FAQs About Diabetes
What are the common risk factors for developing diabetes?
Some common risk factors for developing diabetes include genetics, lifestyle choices such as poor diet and lack of exercise, obesity, and age.
What are the different types of diabetes?
The main types of diabetes are Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Every variety has unique causes and available treatments.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
Typically, blood tests that measure blood glucose levels are used to diagnose diabetes. Other tests, such as the A1C test, may also be used to diagnose diabetes.
What are the complications associated with diabetes?
Complications of diabetes can include heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, vision problems, and skin conditions. Keeping diabetes under control can help avoid these issues.
What are some tips for managing diabetes on a day-to-day basis?
Some tips for managing diabetes include monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, following a healthy diet, staying active, taking medication as prescribed, and seeing your healthcare provider regularly.
Can diabetes be prevented?
While not all cases of diabetes can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. These include abstaining from tobacco use, eating a balanced diet, exercising frequently, and maintaining a healthy weight.
How important is it to follow a treatment plan for diabetes?
Following a treatment plan for diabetes is crucial for managing the condition and preventing complications. It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a plan that works best for you.