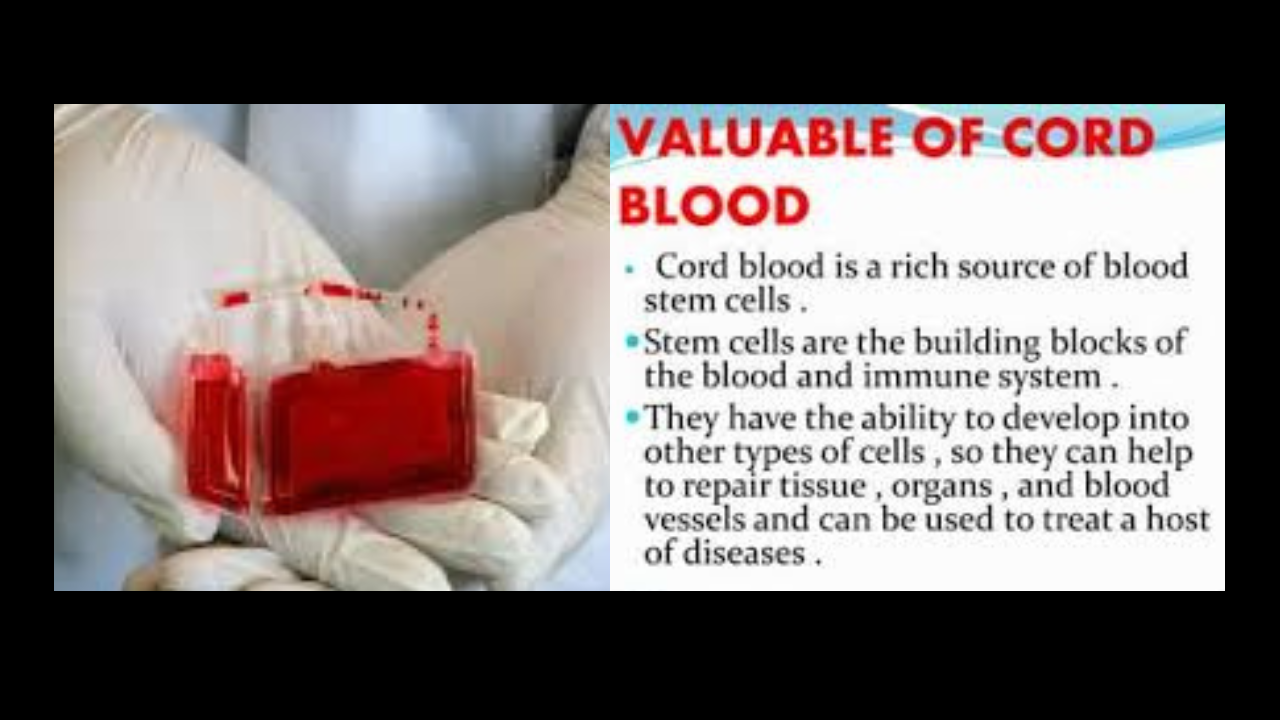
Why is cord blood so valuable?
Benefits of Cord Blood:
Cord blood, a valuable source of stem cells, has shown tremendous potential in treating various medical conditions. The ability of cord blood to regenerate damaged tissues and organs makes it a key player in the field of regenerative medicine. Moreover, cord blood is a non-invasive and painless source of stem cells, making it an attractive option for medical treatments.
Additionally, cord blood storage allows for immediate access to stem cells when needed for treatment. This eliminates the time-consuming process of finding a matched donor for bone marrow transplants. The stored cord blood can be used not only by the baby from whom it was collected but also by family members who are a suitable match, enhancing the likelihood of successful treatment outcomes.
- Cord blood is a valuable source of stem cells with tremendous potential in treating various medical conditions.
- Cord blood has the ability to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, making it essential in regenerative medicine.
- It is a non-invasive and painless source of stem cells, making it an attractive option for medical treatments.
- Cord blood storage allows for immediate access to stem cells when needed for treatment.
- Eliminates the time-consuming process of finding a matched donor for bone marrow transplants.
- Stored cord blood can be used not only by the baby from whom it was collected but also by suitable family members, increasing successful treatment outcomes.
The Medical Importance of Cord Blood
Umbilical cord stem cells play a crucial role in the field of medicine due to their unique ability to differentiate into various types of cells, offering a promising source for regenerative therapies. The practice of umbilical cord preservation has gained traction in recent years as it allows for the collection and storage of these valuable stem cells for potential future use in treating a variety of medical conditions.
The medical community recognizes the significance of umbilical cord stem cells as a valuable resource in regenerative medicine, offering hope for patients with conditions ranging from blood disorders to autoimmune diseases. By harnessing the power of these stem cells through umbilical cord preservation, researchers and healthcare providers are exploring innovative treatment options that could potentially revolutionize the way we approach certain medical conditions.
- Umbilical cord stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various types of cells
- Preservation of umbilical cord allows for collection and storage of valuable stem cells
- Stem cells from umbilical cord offer hope for patients with blood disorders and autoimmune diseases
- Researchers and healthcare providers are exploring innovative treatment options using umbilical cord stem cells
Potential Uses of Cord Blood in Treatments
Cord blood stem cells have shown great promise in treating a variety of medical conditions. Researchers have been exploring their potential use in regenerative medicine, particularly in the repair of damaged tissues and organs. The unique properties of cord blood stem cells make them valuable for treating conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, and other blood disorders.
One notable institution in this field is the New England Cord Blood Bank, which specializes in collecting and storing cord blood for potential future use in treatments. Their work highlights the growing importance of cord blood stem cells in the field of medicine, offering hope for improved outcomes for patients in need of stem cell therapy.
- Cord blood stem cells have shown promise in treating medical conditions
- Researchers are exploring their use in regenerative medicine for repairing damaged tissues and organs
- Unique properties make cord blood valuable for treating leukemia, lymphoma, and other blood disorders
- New England Cord Blood Bank specializes in collecting and storing cord blood for future treatments
- Growing importance of cord blood stem cells offers hope for improved outcomes for patients
The Unique Composition of Cord Blood
Cord blood, a valuable source of stem cells obtained from the umbilical cord after childbirth, possesses a unique composition that sets it apart from other sources like bone marrow. The umbilical cord stem cells contained within cord blood are highly versatile and have the potential to differentiate into various types of cells, making them a promising resource for regenerative medicine and potential treatments for a range of diseases.
Furthermore, the cost of cord blood banking has become more affordable in recent years, making it a viable option for families looking to invest in their future health. With advancements in technology and increased awareness of the benefits of cord blood, more parents are opting to store their child’s cord blood for potential future use. The unique composition of cord blood, combined with its relative accessibility in terms of cost, highlights its growing importance in the field of medical research and treatment options.
- Cord blood contains a high concentration of hematopoietic stem cells, which are crucial for the production of blood cells
- Unlike bone marrow, cord blood can be easily collected without any harm to the mother or baby
- Cord blood also contains other types of stem cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells, which have shown potential in regenerative medicine therapies
- The unique composition of cord blood makes it an attractive option for personalized medicine and treatment options
Cord Blood vs. Bone Marrow: a Comparison
Cord blood and bone marrow are both valuable sources of stem cells used in medical treatments. While cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord after a baby is born, bone marrow is extracted from the center of bones, such as the hip bone. One key advantage of cord blood is its easier collection process compared to bone marrow, which can be a more invasive procedure. Additionally, cord blood is readily available for use when needed, while bone marrow may require time to find a matching donor.
When considering cord blood vs. bone marrow, another point of comparison is the flexibility in storage options. Cord blood can be stored in cord blood banks for future use by the donor or their family members. On the other hand, bone marrow must typically be sourced from a donor at the time of need, making cord blood a more convenient option in terms of tissue storage. Furthermore, cord blood banks often provide excellent customer service for clients looking to store their cord blood for potential future medical needs.
- Cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord after a baby is born
- Bone marrow is extracted from the center of bones, such as the hip bone
- Easier collection process for cord blood compared to bone marrow
- Cord blood is readily available when needed, while bone marrow may require time to find a matching donor
- Cord blood can be stored in cord blood banks for future use by the donor or their family members
- Bone marrow must typically be sourced from a donor at the time of need
- Cord blood banks often provide excellent customer service for clients looking to store their cord blood for potential future medical needs
The Process of Collecting and Storing Cord Blood
Cord blood collection is a relatively simple and painless procedure that occurs shortly after the birth of a baby. Once the umbilical cord is clamped and cut, a trained healthcare professional will insert a needle into the cord vein and allow the blood to flow into a collection bag. This process typically takes around 5-10 minutes and poses no risk to the mother or baby.
After the cord blood is collected, it is carefully tested, processed, and stored at a cord blood bank like Americord Blood. The blood is tested for infectious diseases and other factors to ensure its safety for potential future use. Once the testing is complete, the cord blood is cryogenically frozen and stored at ultra-low temperatures to preserve its viability for years to come. This process of collecting and storing cord blood is crucial in providing a valuable resource for potential medical treatments and therapies.
- Cord blood collection is a simple and painless procedure
- A trained healthcare professional inserts a needle into the cord vein to collect the blood
- The process typically takes 5-10 minutes and poses no risk to mother or baby
- After collection, cord blood is tested for infectious diseases and other factors
- It is processed and stored at a cord blood bank like Americord Blood
- The blood is cryogenically frozen at ultra-low temperatures for future use
The process of collecting and storing cord blood is essential in building a valuable resource for potential medical treatments.
Public vs. Private Cord Blood Banking
When considering cord blood banking, one key decision parents face is whether to store the cord blood publicly or privately. Public cord blood banks collect donations from individuals, which are then available for anyone in need of a stem cell transplant. This option offers the chance for individuals in the general population to access potentially life-saving treatments without the burden of cost.
On the other hand, private cord blood banking involves storing a child’s cord blood exclusively for their own use or for a family member. While this option provides the benefit of personalized access to stem cells if needed in the future, it does come with associated costs for collection, processing, and storage. The decision between public and private cord blood banking ultimately depends on individual preferences regarding potential future needs and financial considerations.
- Public cord blood banks collect donations from individuals for anyone in need of a stem cell transplant
- Offers the chance for individuals in the general population to access potentially life-saving treatments without cost
- Private cord blood banking involves storing cord blood exclusively for child’s own use or family member
- Provides personalized access to stem cells if needed in the future
- Associated costs for collection, processing, and storage with private cord blood banking
- Decision between public and private cord blood banking depends on individual preferences regarding potential future needs and financial considerations
The Function of Cord Blood in Regenerative Medicine.
Cord blood has shown great promise in regenerative medicine due to its rich source of stem cells. These stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them valuable in repairing and regenerating damaged tissues and organs. This potential has opened up new avenues for treating a wide range of medical conditions, from neurodegenerative diseases to heart conditions.
Researchers are exploring how cord blood stem cells can be used to promote tissue repair and regeneration in patients suffering from injuries or diseases that impact their quality of life. By harnessing the regenerative properties of cord blood, scientists aim to develop innovative therapies that could revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine. The versatility and regenerative potential of cord blood stem cells offer hope for patients seeking alternative treatment options and pave the way for exciting advancements in medical science.
- Cord blood is a rich source of stem cells with the ability to differentiate into various cell types
- Stem cells from cord blood can repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs
- Potential applications include treating neurodegenerative diseases and heart conditions
Cord Blood vs. Bone Marrow: a Comparison
Cord blood and bone marrow are both valuable sources of stem cells used in medical treatments. While cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord after a baby is born, bone marrow is extracted from the center of bones, such as the hip bone. One key advantage of cord blood is its easier collection process compared to bone marrow, which can be a more invasive procedure. Additionally, cord blood is readily available for use when needed, while bone marrow may require time to find a matching donor.
When considering cord blood vs. bone marrow, another point of comparison is the flexibility in storage options. Cord blood can be stored in cord blood banks for future use by the donor or their family members. On the other hand, bone marrow must typically be sourced from a donor at the time of need, making cord blood a more convenient option in terms of tissue storage. Furthermore, cord blood banks often provide excellent customer service for clients looking to store their cord blood for potential future medical needs.
- Cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord after a baby is born
- Bone marrow is extracted from the center of bones, such as the hip bone
- Easier collection process for cord blood compared to bone marrow
- Cord blood is readily available when needed, while bone marrow may require time to find a matching donor
- Cord blood can be stored in cord blood banks for future use by the donor or their family members
- Bone marrow must typically be sourced from a donor at the time of need
- Cord blood banks often provide excellent customer service for clients looking to store their cord blood for potential future medical needs
The Process of Collecting and Storing Cord Blood
Cord blood collection is a relatively simple and painless procedure that occurs shortly after the birth of a baby. Once the umbilical cord is clamped and cut, a trained healthcare professional will insert a needle into the cord vein and allow the blood to flow into a collection bag. This process typically takes around 5-10 minutes and poses no risk to the mother or baby.
After the cord blood is collected, it is carefully tested, processed, and stored at a cord blood bank like Americord Blood. The blood is tested for infectious diseases and other factors to ensure its safety for potential future use. Once the testing is complete, the cord blood is cryogenically frozen and stored at ultra-low temperatures to preserve its viability for years to come. This process of collecting and storing cord blood is crucial in providing a valuable resource for potential medical treatments and therapies.
- Cord blood collection is a simple and painless procedure
- A trained healthcare professional inserts a needle into the cord vein to collect the blood
- The process typically takes 5-10 minutes and poses no risk to mother or baby
- After collection, cord blood is tested for infectious diseases and other factors
- It is processed and stored at a cord blood bank like Americord Blood
- The blood is cryogenically frozen at ultra-low temperatures for future use
The process of collecting and storing cord blood is essential in building a valuable resource for potential medical treatments.
The Role of Cord Blood in Regenerative Medicine
Cord blood has shown great promise in regenerative medicine due to its rich source of stem cells. These stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, making them valuable in repairing and regenerating damaged tissues and organs. This potential has opened up new avenues for treating a wide range of medical conditions, from neurodegenerative diseases to heart conditions.
Researchers are exploring how cord blood stem cells can be used to promote tissue repair and regeneration in patients suffering from injuries or diseases that impact their quality of life. By harnessing the regenerative properties of cord blood, scientists aim to develop innovative therapies that could revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine. The versatility and regenerative potential of cord blood stem cells offer hope for patients seeking alternative treatment options and pave the way for exciting advancements in medical science.
• Cord blood is a rich source of stem cells with the ability to differentiate into various cell types
• Stem cells from cord blood can repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs
• Potential applications include treating neurodegenerative diseases and heart conditions
• Researchers are exploring how cord blood stem cells can promote tissue repair in patients with injuries or diseases
• The regenerative properties of cord blood offer hope for innovative therapies in regenerative medicine
Cord Blood Research and Breakthroughs
Research on cord blood has led to numerous breakthroughs in the field of regenerative medicine. Scientists have discovered the potential of cord blood stem cells to treat a variety of diseases, including certain types of cancer, genetic disorders, and autoimmune conditions. These findings have opened up new avenues for exploring the therapeutic properties of cord blood and expanding its applications in modern medicine.
Moreover, recent studies have highlighted the role of cord blood in promoting tissue repair and regeneration. Stem cells derived from cord blood have shown promising results in accelerating healing processes and enhancing the body’s ability to recover from injuries or degenerative conditions. This research offers hope for developing innovative treatments that harness the regenerative potential of cord blood to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
• Cord blood research has led to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine
• Potential of cord blood stem cells to treat diseases such as cancer, genetic disorders, and autoimmune conditions
• New avenues for exploring therapeutic properties of cord blood in modern medicine
• Studies show role of cord blood in promoting tissue repair and regeneration
• Stem cells from cord blood accelerate healing processes and enhance recovery from injuries or degenerative conditions
• Research offers hope for developing innovative treatments using regenerative potential of cord blood
The Economic Value of Cord Blood
Cord blood holds significant economic value due to its potential use in various medical treatments. The cost-effectiveness of utilizing cord blood stem cells in therapies for conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, and genetic disorders is a driving force behind its economic importance. Moreover, the ability to store cord blood for future use provides a financial benefit for families seeking to secure potential treatments for unforeseen health issues.
In addition to the direct economic impact of cord blood on medical treatments, the cord blood banking industry itself contributes to the economy through job creation and revenue generation. Public and private cord blood banks play a vital role in collecting, processing, and storing cord blood units, thus supporting a global network of healthcare professionals and researchers. Furthermore, the continuous advancements in regenerative medicine and cord blood research highlight the ongoing economic potential of this valuable biological resource.
• Cord blood stem cells are cost-effective in treating conditions like leukemia and lymphoma
• Storing cord blood for future use provides financial benefits for families
• Cord blood banking industry creates jobs and generates revenue
• Public and private cord blood banks support healthcare professionals and researchers globally
• Ongoing advancements in regenerative medicine highlight economic potential of cord blood
FAQs About Cord Blood
What are the benefits of cord blood?
Cord blood contains valuable stem cells that can be used in medical treatments for a variety of conditions, making it a valuable resource for both the donor and potential recipients.
Why is cord blood considered medically important?
Cord blood contains hematopoietic stem cells, which have the ability to differentiate into various types of blood cells. This makes cord blood a valuable resource for treating diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and other blood disorders.
What are some potential uses of cord blood in treatments?
Cord blood can be used in the treatment of various blood disorders, immune system disorders, and genetic disorders. It is also being researched for its potential in regenerative medicine.
How does cord blood compare to bone marrow?
Cord blood and bone marrow both contain stem cells, but cord blood is easier to collect and store. Cord blood also has a lower risk of rejection in transplant recipients.
How is cord blood collected and stored?
Cord blood is collected immediately after the birth of a baby, either through a simple and painless procedure or through delayed cord clamping. The collected blood is then processed and stored in a cord blood bank for future use.
What is the difference between public and private cord blood banking?
Public cord blood banks store cord blood donations for public use, while private cord blood banks store cord blood for personal use by the donor or their family. Public banks are available to anyone in need of a transplant, while private banks offer exclusive access to the stored cord blood.
How does cord blood play a role in regenerative medicine?
Cord blood is being researched for its potential in regenerative medicine, as its stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various types of cells and tissues. This makes cord blood a promising resource for treating a wide range of medical conditions.
What are some recent breakthroughs in cord blood research?
Recent breakthroughs in cord blood research include advancements in using cord blood stem cells to treat neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and tissue regeneration. Researchers are continually exploring new ways to harness the potential of cord blood in medical treatments.
What is the economic value of cord blood?
The economic value of cord blood lies in its potential to provide cost-effective treatments for a variety of medical conditions. By storing cord blood, individuals can ensure access to potentially life-saving treatments for themselves or their family members in the future.