Understanding Diabetes: Your Friendly Guide to Health
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on diabetes. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with diabetes, it can be overwhelming to navigate the ins and outs of this chronic condition. Our health guide aims to provide you with the knowledge and resources you need to manage your health effectively and live a fulfilling life with diabetes.
Key Takeaways:
- Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
- Managing diabetes requires a proactive approach to lifestyle modifications and treatment.
- Our health guide will explore the different aspects of diabetes, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
- By understanding diabetes, you can take control of your health and live a fulfilling life.
What is Diabetes?
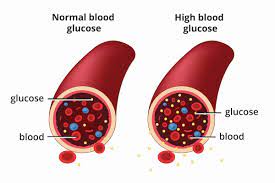
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes glucose, a type of sugar that serves as the body’s primary source of energy. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels) or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to an accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream, which can cause a range of health problems.
There are three main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type of diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. People with type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 diabetes: This type of diabetes accounts for the majority of diabetes cases and occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and lack of physical activity, and may require medication or insulin therapy to manage.
- Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after delivery. Women who have had gestational diabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
While diabetes is a serious medical condition, it is manageable with proper treatment and self-care.
Causes of Diabetes: Understanding the Risk Factors
Diabetes is a complex condition that can be caused by a range of factors. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most common Diabetes causes and risk factors.
Genetics
Family history can play a significant role in the development of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Research suggests that if a person’s parent or sibling has diabetes, their own risk of developing the condition is higher.
Lifestyle Choices
Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as consuming a poor diet, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of developing diabetes. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and sugar can also contribute to weight gain, which is a significant Diabetes risk factor. Maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly can help reduce the risk of developing Diabetes.
Age and Ethnicity
The risk of developing Diabetes increases with age. People aged 45 or older are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. Additionally, ethnicity can also play a role in the development of diabetes. African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian American communities are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes than Caucasians.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that can develop during pregnancy. Women who have had gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. Additionally, babies born to women with gestational diabetes may also be more likely to develop Diabetes later in life.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of Diabetes is the first step towards prevention and management. By making healthy lifestyle choices and working with healthcare professionals to manage any existing health conditions, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing Diabetes and lead a fulfilling life.
Symptoms of Diabetes

Diabetes symptoms can vary depending on the type of diabetes you have. Some of the most common signs and symptoms of diabetes include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Feeling very hungry, even if you have recently eaten
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Cuts or bruises that are slow to heal
- Tingling, pain, or numbness in the hands and feet
These symptoms can develop gradually and may be difficult to notice at first. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to speak with a healthcare professional to get a proper diagnosis and begin treatment.
Tip: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help catch diabetes early, before symptoms become severe.
If left untreated, diabetes can lead to serious complications, including kidney damage, nerve damage, and heart disease. That is why it is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms of diabetes and seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosing Diabetes
Receiving a diabetes diagnosis can be a daunting and overwhelming experience. However, early detection and management of diabetes can help prevent complications and improve overall health outcomes. Healthcare professionals use a variety of tests to diagnose diabetes and determine the best course of treatment.
Diabetes Tests
The primary test used to diagnose diabetes is the A1C test, which measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. A result of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) are also used to diagnose diabetes.
The FPG test measures blood glucose levels after fasting for at least 8 hours. A result of 126 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes. The OGTT involves drinking a sugary solution, then measuring blood glucose levels 2 hours later. A result of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
Diabetes Diagnosis
It is important to note that a single positive test result does not necessarily mean a diabetes diagnosis. Healthcare professionals will usually order a second confirmatory test before diagnosing diabetes. Additionally, some individuals may have high blood glucose levels but not meet the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, which is known as prediabetes.
If you receive a diabetes diagnosis, your healthcare team will work with you to develop an individualized treatment plan to manage your diabetes and prevent complications. Regular monitoring and self-care practices are essential for successful diabetes management.
Managing Diabetes
Effective diabetes management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication. The goal is to keep your blood sugar levels within a target range, which can vary depending on the individual and type of diabetes. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.
Lifestyle Modifications
Your healthcare team may recommend the following lifestyle modifications:
-
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet:
It’s important to eat a diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Avoiding processed, sugary, and high-fat foods is also crucial. A registered dietitian can help you create a personalized meal plan that fits your needs and preferences.
-
- Engaging in regular physical activity:
Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and promote overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Consult with your doctor before starting any exercise program.
-
- Maintaining a healthy weight:
Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing diabetes and other health conditions. Losing even a small amount of weight can improve blood sugar control and reduce your risk of complications.
-
- Managing stress:
Stress can cause blood sugar levels to rise, so finding healthy ways to manage stress is essential. Consider practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
-
- Monitoring blood sugar levels:
Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels can help you track how well your diabetes management plan is working and adjust as needed.
Medication
If lifestyle modifications alone are not enough to manage your diabetes, your healthcare team may prescribe medication to help control your blood sugar. The type of medication will depend on the type of diabetes you have, your blood sugar levels, and other medical conditions you may have.
Some common medications used to treat diabetes include:
| Medication Type | How it Works | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Decreases glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity | Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort |
| Insulin | Replaces the insulin your body is not producing enough of or not using effectively | Hypoglycemia, weight gain, injection site reactions |
| Sulfonylureas | Stimulate the pancreas to secrete more insulin | Hypoglycemia, weight gain |
It’s essential to take medication as prescribed and monitor your blood sugar levels closely to avoid potential complications.
Managing diabetes can be challenging, but with the right tools and support, it’s possible to live a healthy, fulfilling life. Work closely with your healthcare team and don’t hesitate to reach out for help when you need it.
Preventing Diabetes: Making Lifestyle Changes for a Healthier You
If you have a family history of diabetes, you are at a higher risk of developing the disease. However, making positive lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
Healthy Eating Habits
One of the most effective ways to prevent diabetes is to maintain healthy eating habits. This can be achieved by choosing foods that are low in sugar, saturated fats, and refined carbs. Instead, opt for foods that are rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
| Food Options | Avoid |
|---|---|
| Fruits | Sugary drinks and snacks |
| Vegetables | Processed foods |
| Whole grains | Saturated fats |
| Lean proteins | Refined carbs |
Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can also play a significant role in preventing diabetes. It helps improve insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise per day, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Intake
Smoking can increase your risk of developing diabetes, as it can affect insulin production and increase inflammation. Limiting alcohol intake is also important, as alcohol can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of developing diabetes.
Manage Your Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial in preventing diabetes. Being overweight or obese can increase insulin resistance, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. By making healthy food choices and engaging in regular physical activity, you can help maintain a healthy weight.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups can also play a crucial role in preventing diabetes. By monitoring your blood sugar levels and identifying any potential warning signs, you can take proactive steps towards preventing diabetes.
By making these simple lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes and improve your overall health and wellbeing.
Living with Diabetes: Tips and Resources for Diabetes Support

Being diagnosed with diabetes can be overwhelming, but with the right tools and support, it is possible to live a full and healthy life. Here are some tips and resources to help you manage your diabetes:
Self-Care Practices
Self-care is essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications. Here are some self-care practices to help you stay healthy:
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly
- Eat a well-balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Exercise regularly (with your doctor’s approval)
- Take medication as prescribed
- Get enough sleep
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation
Emotional Support
Receiving emotional support can help you cope with the challenges of living with diabetes. Here are some resources for emotional support:
“It’s not easy, but it’s worth it. Managing your diabetes well will help you feel better and lower your risk of complications.”
- Join a support group for people with diabetes
- Seek counseling or therapy
- Talk to friends and family about your diabetes and how they can support you
Resources for Assistance
There are many resources available to assist you in managing your diabetes. Here are some resources to consider:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| American Diabetes Association | A nonprofit organization that provides education and support for people with diabetes |
| Diabetes Self-Management Education | Classes and programs that teach you how to manage your diabetes |
| Diabetes Prevention Program | A lifestyle change program designed to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes |
| Medicare Diabetes Prevention Program | A program designed to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes for Medicare beneficiaries |
Remember, living with diabetes requires ongoing management and support. With the right tools and resources, you can effectively manage your diabetes and live a healthy, fulfilling life.
Conclusion
We hope that this guide has provided you with valuable insights into understanding and managing diabetes. Remember that diabetes is a manageable condition and with the right approach, you can live a fulfilling life while keeping your health in check.
Stay Proactive
The key to living well with diabetes is to stay proactive. Stay committed to healthy habits like regular exercise and a balanced diet. Make sure to attend regular check-ups with your healthcare professionals and follow their advice on managing your condition effectively. With the right approach, you can ensure that diabetes does not hold you back from living your life to the fullest.
Find Support
Living with diabetes can sometimes feel overwhelming, but remember that you are not alone. Reach out to support groups or organizations that offer resources and assistance for people with diabetes. Don’t hesitate to seek emotional support from your loved ones or mental health professionals if you feel overwhelmed or anxious.
Empower Yourself
Empower yourself with knowledge and understanding of diabetes. Stay informed about the latest developments in diabetes research and treatment options. Take control of your health and make informed decisions about managing your diabetes.
Thank You
Thank you for reading this guide and we hope you found it useful. Remember that diabetes is a manageable condition and with the right approach, you can live a happy and healthy life.
FAQ
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. It occurs when the pancreas either does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
What are the different types of diabetes?
The main types of diabetes are type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is a condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after giving birth.
What are the causes of diabetes?
The causes of diabetes can vary depending on the type. Type 1 diabetes is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by lifestyle factors such as being overweight or obese, sedentary behavior, and poor diet. Gestational diabetes is thought to be related to hormonal changes during pregnancy.
What are the common symptoms of diabetes?
Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, increased thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and frequent infections. However, it’s important to note that some individuals may not experience any symptoms or may have mild symptoms.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
Diabetes is typically diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels. The most common tests include fasting plasma glucose (FPG), oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test.
How can diabetes be managed?
Diabetes management involves maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring blood sugar levels, taking prescribed medications, and managing stress levels.
Can diabetes be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through healthy lifestyle choices. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, being physically active, eating a nutritious diet, and avoiding tobacco use.
What support is available for those living with diabetes?
There are various resources and support systems available for individuals living with diabetes. This can include diabetes education programs, support groups, online communities, and healthcare professionals specializing in diabetes management. It’s important to reach out for support and take advantage of the available resources.

